The term sustainability is used to indicate programs, initiatives, and actions aimed at the preservation of resources. However, it actually refers to four distinct areas: human, social, economic and environmental – known as the four pillars of sustainability.
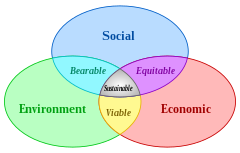
Venn diagram of sustainable development:
at the confluence of three constituent parts: Image from Wikipedia

The four domains of social sustainability according to the Circles of Sustainability approach used by the United Nations
Human sustainability
Human sustainability aims to maintain and improve the human capital in society. Investments in the health and education systems, access to services, nutrition, knowledge (as we are fast becoming a knowledge society), and skills are all programs under the umbrella of human sustainability. Natural resources and spaces available are limited and there is a need to balance continual growth with improvements to health and achieving economic wellbeing for everyone. Human sustainability focuses on the importance of anyone directly or indirectly involved in the making of products, or provision of services or broader stakeholders (the human capital of the organization) (Benn et al., 2014). Communities around the globe may be positively or negatively affected by business activities or impacted through methods used to source raw materials. Human sustainability encompasses the development of skills and human capacity to support the functions and sustainability of the organization and to promote the well-being of communities and society.
Social sustainability
Social life is the least defined and least understood of the different ways of approaching sustainability and sustainable development. Social sustainability has had considerably less attention in public dialogue than economic and environmental sustainability.
Social sustainability aims to preserve social capital by investing, maintaining and creating services that constitute the framework of our society. The concept envisages a larger view of the world in relation to communities, cultures, and globalisation. Culture and globalization are one of the main determinants of the tourism industry.
It means to preserve resources for future generations and to acknowledge that what we do can have an impact on others. Social sustainability focuses on maintaining and improving social quality with concepts such as cohesion, reciprocity and honesty and the importance of relationships amongst people. It can be encouraged and supported by laws, information and shared ideas of equality and rights. Social sustainability incorporates the idea of sustainable development as defined by the United Nations sustainable development goals. The principle of sustainable development addresses social and economic improvement that protects the environment and supports equality, and therefore the economy and society and the ecological system are mutually dependent (Diesendorf, 2000).
Economic sustainability
The economic sustainability is the ability of an economy to support a defined level of economic production indefinitely. It aims to maintain the capital intact. If social sustainability focuses on improving social equality, economic sustainability aims to improve the standard of living. In the context of business, it refers to the efficient use of assets to maintain company profitability over time. As stated by the UK Government (Annual Report 2000, January 2001):
“Maintaining high and stable levels of economic growth is one of the key objectives of sustainable development. Abandoning economic growth is not an option. But sustainable development is more than just economic growth. The quality of growth matters as well as the quantity.”
Environmental sustainability
Environmental sustainability aims to improve human welfare through the protection of natural resources. Initiatives and programs are defined as environmentally sustainable when they ensure that the needs of the population are met without the risk of compromising the needs of future generations. Environmental sustainability, as described by Dunphy, Benveniste, Griffiths, and Sutton (2000) place emphasis on how business can achieve positive economic outcomes without doing any harm, in the short- or long-term, to the environment. According to Dunphy et al. (2000) an environmentally sustainable business seeks to integrate all four sustainability pillars and to reach this aim each one needs to be treated equally.
The principle of the four pillars of sustainability states that for complete sustainability problems to be solved in relation to all four pillars of sustainability and then need be maintained. Although in some cases these may overlap, it is important to identify the specific type of green business to focus on, as the four types present unique characteristics. Businesses need to make a strategic decision about it so as to effectively incorporate the chosen approach into their policies and procedures.
Source(s) and Link(s):
https://www.futurelearn.com/courses/sustainable-business/1/steps/157438
Wikipedia
