Petroleum accumulates in specific geological settings where the right combination of source rock, reservoir rock, caprock, and structural or stratigraphic traps are present. The most likely geology for petroleum bearing includes sedimentary basins with particular rock types and structures.
Key Petroleum-Bearing Geologies
- Source Rocks: These are usually organic-rich shales or limestones formed from ancient sediments deposited in environments with abundant organic material, such as lakes or marine basins. Over millions of years and under heat and pressure, this organic matter transforms into hydrocarbons.
- Reservoir Rocks: The most common reservoir rocks are porous and permeable sandstones and carbonates (limestones, dolomites). These rocks allow for the storage and migration of petroleum. Reservoir rocks must have sufficient porosity (space to hold oil) and permeability (pathways for fluids to move).
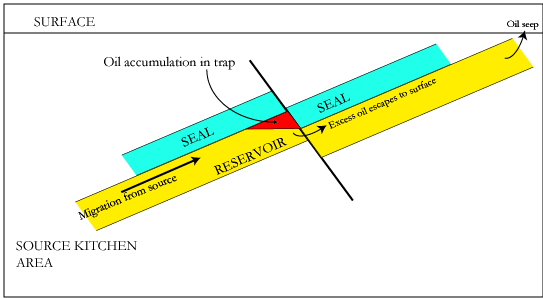
- Caprocks: Impermeable rocks, like shale or evaporites, act as a seal above reservoir rocks, preventing hydrocarbons from escaping to the surface.
- Traps: Petroleum accumulates in traps formed by either structural deformation (folds, faults, salt domes) or changes in rock type (stratigraphic traps, such as buried river channels or reefs). Examples include anticlines, fault traps, and salt dome traps.
Examples of Petroleum Geology
- Classic petroleum provinces, such as the Gulf of Suez, contain reservoirs in Cretaceous sandstones and carbonates.
- North Sea oil fields have Jurassic sandstones, Triassic alluvial plain deposits, Paleogene deep-sea fans, and chalk reservoirs.
- Sandstone, often with secondary silica overgrowth or dolomitization, is the most common reservoir especially in regions like India.
- Petroleum fields may also occur in fractured carbonates, reef limestones, and chalks.
Typical Sequence for Oil Fields


Fault Trap
Sedimentary basins with organic-rich source rocks, porous and permeable reservoir rocks, effective caprocks, and robust trapping mechanisms are the ideal geological settings for petroleum accumulation and extraction.
read more here
